Understanding Results
As Querri analyzes your data, it produces results in various formats. This guide helps you understand and work with these results effectively.
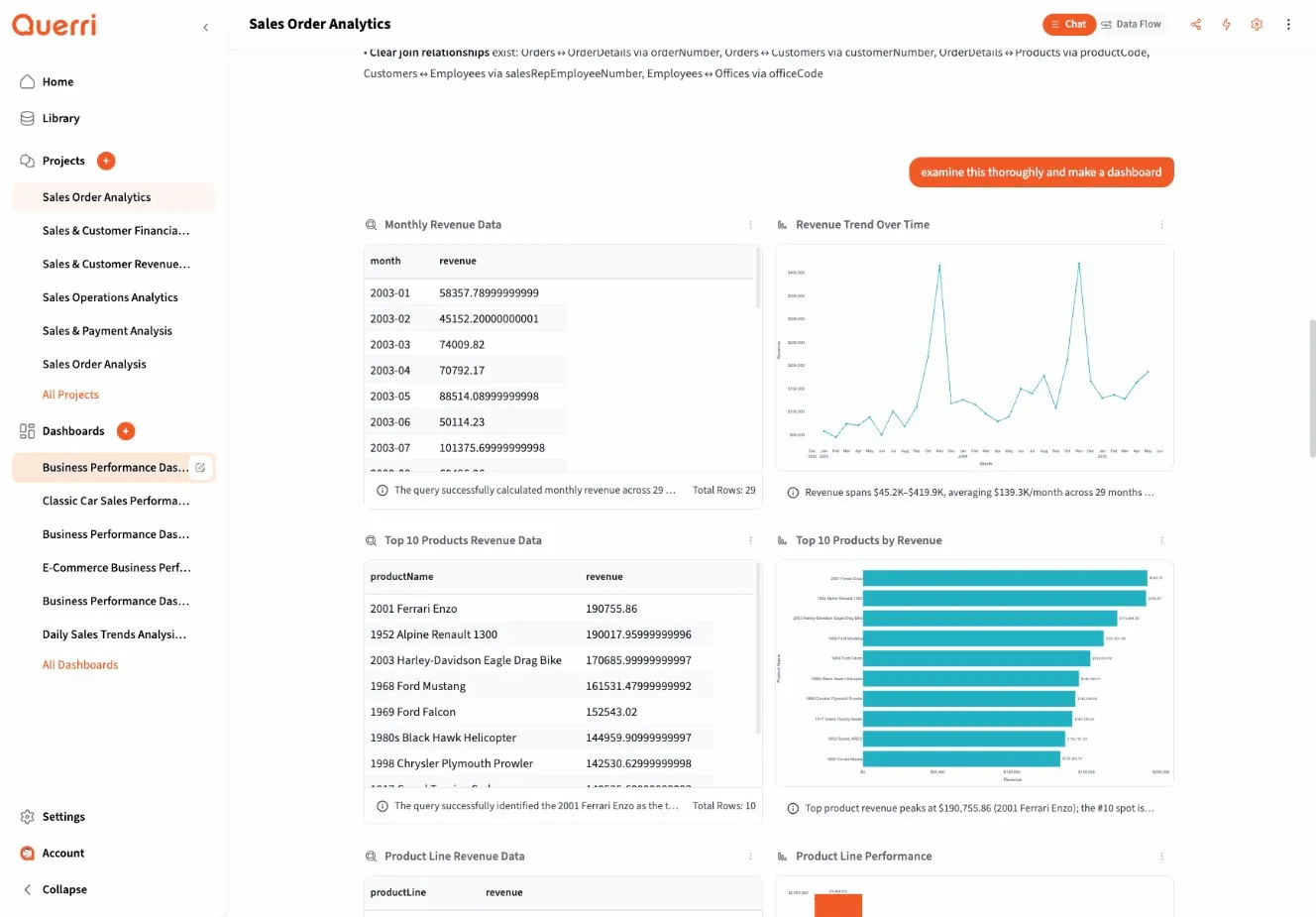
Types of Results
Section titled “Types of Results”Querri can display results in three primary formats:
Table Results (QDF)
Section titled “Table Results (QDF)”Tabular data appears in the QDF (Querri Data Frame) viewer:
- Interactive scrolling: Navigate through rows and columns
- Column headers: Click to understand data types
- Clean formatting: Numbers, dates, and text are properly formatted
- Large dataset support: Handles thousands of rows smoothly
Tables are the most common result type, used for:
- Raw data previews
- Filtered datasets
- Aggregated summaries
- Joined or transformed data
Charts and Visualizations
Section titled “Charts and Visualizations”Visual results appear as interactive charts:
- Multiple chart types: Bar, line, scatter, area, pie, and more
- Readable legends: Understand what each element represents
- Tooltips: Hover for detailed values
- Responsive sizing: Charts adapt to your screen
Visualizations help you spot trends, patterns, and outliers quickly.
Text Insights
Section titled “Text Insights”Some results are textual explanations:
- Summary statistics: “Average revenue: $45,234”
- Answers to questions: “There are 1,247 unique customers”
- Interpretations: “Revenue increased 23% year-over-year”
- Recommendations: “Consider filtering outliers before forecasting”
Text results provide context and explanations alongside data.
Reading the QDF Viewer
Section titled “Reading the QDF Viewer”The QDF viewer is Querri’s table interface. Here’s how to use it:
Navigation
Section titled “Navigation”- Scroll vertically: See more rows
- Scroll horizontally: See more columns
- Pagination: For very large datasets, navigate between pages
Understanding Columns
Section titled “Understanding Columns”Each column header shows:
- Column name: What the data represents
- Data type: Number, text, date, boolean, etc.
- Sort options: Click to sort ascending or descending (when available)
Cell Values
Section titled “Cell Values”Individual cells display:
- Numbers: Formatted with appropriate decimals and separators
- Dates: In human-readable format
- Text: Truncated with ellipsis if too long (hover for full value)
- Null values: Shown as empty or “null”
Row Counts
Section titled “Row Counts”The viewer typically shows:
- Total number of rows
- Current page or range displayed
- Any filters applied
Understanding Charts
Section titled “Understanding Charts”When a step produces a visualization, here’s what to look for:
Chart Components
Section titled “Chart Components”Title: Describes what the chart shows Axes: X-axis (horizontal) and Y-axis (vertical) with labels Legend: Explains colors, lines, or segments Data points/bars/lines: The actual visual representation
Interactive Features
Section titled “Interactive Features”Many charts support:
- Hover tooltips: Exact values when you mouse over elements
- Zoom: Click and drag to zoom into specific areas (when supported)
- Pan: Navigate around zoomed charts
Reading Common Chart Types
Section titled “Reading Common Chart Types”Line charts: Show trends over time. Look for slopes (increasing/decreasing) and inflection points.
Bar charts: Compare values across categories. Height represents magnitude.
Scatter plots: Show relationships between two variables. Patterns indicate correlation.
Pie charts: Display proportions of a whole. Size represents percentage.
Area charts: Like line charts but with filled areas, good for showing cumulative values.
Step Status Indicators
Section titled “Step Status Indicators”Each step in your project shows its status:
Running
Section titled “Running”Indicator: Spinner or progress animation Meaning: The step is currently executing Action: Wait for completion
Steps usually complete in seconds, though complex queries or large datasets may take longer.
Success
Section titled “Success”Indicator: Green checkmark or success icon Meaning: The step completed without errors Results: Available to view below the step
Most steps should complete successfully. Review the results to ensure they match your expectations.
Indicator: Red X or error icon Meaning: The step encountered a problem and couldn’t complete Information: Error message explains what went wrong
Common causes of errors:
- Invalid column names
- Data type mismatches
- Missing data sources
- Syntax issues in complex operations
When you see an error:
- Read the error message carefully
- Identify what went wrong
- Ask the AI to fix it or rephrase your question
- Continue with your analysis
The AI can usually recover from errors and continue.
Downloading Results
Section titled “Downloading Results”You can export results for use outside Querri:
Downloading Tables
Section titled “Downloading Tables”For QDF table results:
- Look for a Download or Export button
- Select format (typically CSV or Excel)
- Save to your computer
Use downloaded data in:
- Spreadsheet applications
- Other analysis tools
- Reports and presentations
- Archival purposes
Downloading Charts
Section titled “Downloading Charts”For visualizations:
- Find the Download or Export option
- Choose format (PNG, JPEG, SVG, or PDF)
- Save the image
Use exported charts in:
- Presentations
- Reports
- Dashboards
- Publications
Downloading Full Projects
Section titled “Downloading Full Projects”Some interfaces let you export entire project:
- All steps and their results
- Data sources used
- Complete analysis narrative
This is useful for:
- Archiving completed work
- Sharing with non-Querri users
- Regulatory compliance
Copying Data
Section titled “Copying Data”For quick access to results:
Copy Table Data
Section titled “Copy Table Data”- Select cells in the QDF viewer (if supported)
- Right-click and Copy, or use Ctrl+C / Cmd+C
- Paste into spreadsheets, documents, or other tools
Copy Chart Images
Section titled “Copy Chart Images”- Right-click on a chart
- Select “Copy image” or similar option
- Paste into documents or image editors
Copy Text Results
Section titled “Copy Text Results”Simply select and copy text insights like any other text on the web.
Interpreting Results in Context
Section titled “Interpreting Results in Context”Understanding individual results is important, but so is seeing the bigger picture:
Sequential Steps
Section titled “Sequential Steps”Results build on each other:
- Step 1 loads data (1,000 rows)
- Step 2 filters to 2024 (800 rows)
- Step 3 aggregates by month (12 rows)
- Step 4 creates chart (visual of 12 data points)
Watch how data transforms through the sequence.
Validating Results
Section titled “Validating Results”Ask yourself:
- Do these numbers make sense? Check for obvious errors.
- Is this what I expected? Unexpected results might reveal insights or issues.
- Should I verify? Cross-reference with source data when critical.
Following the Thread
Section titled “Following the Thread”In a conversational analysis:
- Each result answers part of your question
- Results may raise new questions
- The conversation builds understanding incrementally
Don’t just look at the final result—the journey provides context.
Common Result Patterns
Section titled “Common Result Patterns”Empty Results
Section titled “Empty Results”If a step returns no rows:
- Your filter might be too restrictive
- There might be a data type issue (e.g., date format)
- The data simply might not contain what you’re looking for
Action: Broaden your filter or check your data.
Unexpected Row Counts
Section titled “Unexpected Row Counts”If you get far more or fewer rows than expected:
- Check for duplicates (more rows)
- Verify your filter conditions (fewer rows)
- Look for join issues (often multiplies rows)
Action: Ask the AI to explain the row count or adjust your query.
Strange Values
Section titled “Strange Values”If you see odd numbers, dates, or text:
- Data types might be misinterpreted
- Source data might have quality issues
- Calculations might need adjustment
Action: Use data cleaning steps or ask the AI to handle the issue.
Best Practices
Section titled “Best Practices”Review Each Step
Section titled “Review Each Step”Don’t skip ahead—look at each step’s results:
- Catch errors early
- Understand the analysis flow
- Verify assumptions
Spot Check Data
Section titled “Spot Check Data”For important analyses:
- Compare a few results to source data manually
- Check that aggregations make sense
- Verify calculations with a calculator
Ask Questions About Results
Section titled “Ask Questions About Results”If something looks off:
- “Why are there only 3 rows here?”
- “What does this null value mean?”
- “Can you explain this outlier?”
The AI can help interpret results.
Save Important Results
Section titled “Save Important Results”Don’t rely solely on the project:
- Download critical tables
- Export key visualizations
- Take screenshots of important insights
This creates a backup and makes sharing easier.
Next Steps
Section titled “Next Steps”- Learn how to create better visualizations
- Explore project management to organize your work
- Understand sharing options to collaborate on results